Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The
kinetic energy of an object increases as its ____ increases. a. | gravitational
energy | c. | specific
heat | b. | potential
energy | d. | velocity | | | | |
|
|
|
2.
|
The
SI unit for energy is the ____. a. | calorie | c. | meter per second | b. | joule | d. | kilogram | | | | |
|
|
|
3.
|
According to the law of conservation of energy, the total amount of energy in the
universe ____. a. | remains constant | c. | increases | b. | changes
constantly | d. | decreases | | | | |
|
|
|
4.
|
In a
chemical change, energy can be _____. a. | created, but not destroyed | c. | either created or destroyed | b. | destroyed, but
not created | d. | neither created
nor destroyed | | | | |
|
|
|
5.
|
The
two terms below that are identical in meaning are _____. a. | calorie and
Calorie | c. | Calorie and
joule | b. | calorie and joule | d. | kilocalorie and Calorie | | | | |
|
|
|
6.
|
If
the heat of reaction is negative, the reaction is _____. a. | endothermic | c. | negative | b. | exothermic | d. | positive | | | | |
|
|
|
7.
|
A
burger contains 220 nutritional Calories. Convert this energy into joules. a. | 9.2 ´ 10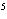 J J | c. | 2.2 ´ 10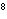 J J | b. | 9.2 ´ 10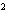 J
J | d. | 5.5 ´ 10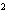 J J | | | | |
|
|
|
8.
|
Rice
contains 245 nutritional Calories. Calculate the energy in joules.
|
|
|
9.
|
What
is the energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1ºC or 1
K? a. | specific
heat | c. | heat
capacity | b. | heat energy | d. | enthalpy of formation | | | | |
|
|
|
10.
|
A 4.0
g sample of iron was heated from 0ºC to 20.ºC. It absorbed 35.2 J of energy as heat. What
is the specific heat of this piece of iron? a. | 2816 J/(g·ºC) | c. | 2.27 J/g | b. | 2.27
J/(g·ºC) | d. | 0.44
J/(g·ºC) | | | | |
|
|
|
11.
|
How
much energy does a copper sample absorb as energy in the form of heat if its specific heat is 0.384
J/(g·ºC), its mass is 8.00 g, and it is heated from 10.0ºC to
40.0ºC? a. | 0.0016
J/(g·ºC) | c. | 92.2
J | b. | 0.0016
J | d. | 92.2
J/(g·ºC) | | | | |
|
|
|
12.
|
Find
the specific heat of a material if a 6.0 g sample absorbs 50. J when it is heated from 30ºC to
50ºC. a. | 0.60
J | c. | 0.42
J | b. | 0.60
J/(g·ºC) | d. | 0.42
J/(g·ºC) | | | | |
|
|
|
13.
|
How
much energy is absorbed as heat by 20. g of gold when it is heated from 25ºC to 35ºC? The
specific heat of gold is 0.13 J/g·ºC. a. | 26 J | c. | 0.0006 J | b. | 26
J/(g·ºC) | d. | 0.0006
J/(g·ºC) | | | | |
|
|
|
14.
|
A 5.0
g sample of silver is heated from 0ºC to 35ºC and absorbs 42 J of energy as heat. What is
the specific heat of silver? a. | 0.24 J | c. | 0.74 J | b. | 0.24
J/(g·ºC) | d. | 0.74
J(g·ºC) | | | | |
|
|
|
15.
|
The
Greek letter D stands
for a. | "heat
stored in." | c. | "rate
of." | b. | "mass of." | d. | "change in." | | | | |
|
|
|
16.
|
What
would likely happen if you were to touch the flask in which an endothermic reaction were
occurring? a. | The flask would
probably feel cooler than before the reaction started. | b. | The flask would
probably feel warmer than before the reaction started. | c. | The flask would
feel the same as before the reaction started. | d. | none of the
above | | |
|
|
|
17.
|
When
energy is changed from one form to another, ____. a. | some of the energy is lost entirely | b. | all of the
energy can be accounted for | c. | a physical change occurs | d. | all of the
energy is changed to a useful form | | |
|
|
|
18.
|
A
process that absorbs heat is a(n) ____. a. | endothermic process | c. | exothermic process | b. | polythermic
process | d. | ectothermic
process | | | | |
|
|
|
19.
|
How
many joules are in 148 calories? (1 cal = 4.18 J) a. | 6.61 J | c. | 148 J | b. | 35.4
J | d. | 619
J | | | | |
|
|
|
20.
|
The
specific heat of silver is 0.24 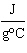 . How many joules of
energy are needed to warm 4.37 g of silver from 25.0 . How many joules of
energy are needed to warm 4.37 g of silver from 25.0 C to 27.5 C to 27.5 C? C? a. | 2.62
J | c. | 45.5
J | b. | 0.14
J | d. | 0.022
J | | | | |
|
|
|
21.
|
Calculate the kinetic energy in J of an electron (mass = 9.11 x 10-28 kg)
moving at 6.00 x 106 m/s. a. | 4.98 x 10-48 | d. | 2.49 x 10-48 | b. | 3.28 x
10-14 | e. | 6.56 x
10-14 | c. | 1.64 x 10-14 | | | | |
|
|
|
22.
|
The
kinetic energy of a 7.3 kg steel ball traveling at 18.0 m/s __________ J. a. | 1.2 x
103 | d. | 1.3 x
102 | b. | 66 | e. | 7.3 | c. | 2.4 x 103 | | | | |
|
|
|
23.
|
Calculate the kinetic energy (J) of a 150 lb jogger (68.1 kg) traveling at 12.0
mile/hr (5.36 m/s). a. | 1.96 x 103 | d. | 183 | b. | 365 | e. | 68.1 | c. | 978 | | | | |
|
|
|
24.
|
Determine the kinetic energy (J) of an 80.0 g bullet traveling at 300.0
m/s. a. | 3.60 x
106 | d. | 12.0 | b. | 1.20 x 104 | e. | 80.0 | c. | 3.60 x 103 | | | | |
|
|
|
25.
|
Work
equals force _____ distance. a. | plus | d. | divided by | b. | times | e. | combined
with | c. | minus | | | | |
|
|
|
26.
|
One
Joule equals __________. a. | 1 kgm2/s2 | d. | 1 gcm/s | b. | 2
kg | e. | none of
these | c. | 4.184 cal | | | | |
|
|
|
27.
|
At
what velocity (m/s) must a 20.0 g object be moving in order to possess a kinetic energy of 1.00
J? a. | 1.00 | d. | 1.00 x
103 | b. | 100 x 102 | e. | 50.0 | c. | 10.0 | | | | |
|
|
|
28.
|
How
much kinetic energy (in J) is possessed by a 23.2 g object moving at a speed of 81.9
km/hr? a. | 1900 | d. | 1.43 x
10-3 | b. | 77.8 | e. | 6.00 | c. | 145 | | | | |
|
|
|
29.
|
At
what speed must a 35.0 mg object be moving in order to possess 1.20 J of kinetic
energy? a. | 0.262
km/hr | d. | 943
km/hr | b. | 15.7 km/hr | e. | 26.9 km/hr | c. | 262
km/hr | | | | |
|
|
|
30.
|
The
first law of thermodynamics states that __________. a. | all spontaneous
processes are accompanied by an increase in disorder | b. | energy is
conserved during any process | c. | the entropy of a pure, crystalline substance at absolute zero
is zero | d. | the amount of work done during a change is independent of the
pathway of that change | e. | none of these | | |
|
|
|
31.
|
What
is the DE (in J) of a
system that releases 12.4 J of heat and does 4.2 J of work on the surroundings? a. | 16.6 | d. | -16.6 | b. | 12.4 | e. | -8.2 | c. | 4.2 | | | | |
|
|
|
32.
|
The
value of DE for a system that performs 213 kJ of work on its surroundings and loses 79 kJ of
heat is __________ kJ. a. | +292 | d. | -134 | b. | -292 | e. | -213 | c. | +134 | | | | |
|
|
|
33.
|
Calculate the value of DE (in J) for a system that loses 50 J of heat and has 150 J of work
performed on it by the surroundings. a. | 50 | d. | -200 | b. | 100 | e. | +200 | c. | -100 | | | | |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which
of the following is a statement of the first law of thermodynamics? a. | Ek =
1/2mv2 | b. | a negative DH corresponds to an exothermic process | c. | DE = Efinal - Einitial | d. | Energy lost by
the system must be gained by the surroundings. | e. | 1 cal = 4.184 J
(exactly) | | |
|
|
|
35.
|
A
_____ q corresponds to an _____ process. a. | negative, endothermic | d. | zero, exothermic | b. | negative,
exothermic | e. | zero,
endothermic | c. | positive, exothermic | | | | |
|
|
|
36.
|
What
is the change in the internal energy (in J) of a system that absorbs 2,500 J of heat and that does
7,655 J of work on the surroundings? a. | 10,155 | d. | -10,155 | b. | 5,155 | e. | 1.91 x
107 | c. | -5,155 | | | | |
|
|
|
37.
|
What
is the change in the internal energy (in J) of a system that releases 2,500 J of heat and that does
7,655 J of work on the surroundings? a. | -10,155 | d. | 10,155 | b. | -5,155 | e. | 5,155 | c. | -1.91 x 107 | | | | |
|
|
|
38.
|
When
a sample of aluminum absorbed 9.86 J of heat, its temperature increased from 23.2°C to
30.5°C. Since the specific heat of aluminum is 0.90 J/g-K, the mass of the sample was
_____ g.
|
|
|
39.
|
When
72 g of a metal at 97.0°C is added to 100.0 g of water at 25.0°C, the final temperature is
29.1°C. What is the heat capacity (in J/g-K) of the metal? The specific heat of
H2O(l) is 4.18 J/g-K. a. | 0.46 | d. | 2.0 | b. | 2.8 | e. | 4.18 | c. | 0.35 | | | | |
|
|
|
40.
|
Calculate the heat capacity (in J/g-K) for metal X from the following
information. A sample of the metal (95 g) at 75.0°C is placed in 50.0 g of water at
18.0°C. The specific heat of H2O(l) is 4.18 J/g-K. The final temperature of the
water is 23.0°C. a. | 23 | d. | 3.6 | b. | 0.21 | e. | 4.2 | c. | 0.76 | | | | |
|
|
|
41.
|
The
specific heat of copper metal is 0.38 J/g-K. Assume you had a 75 g cube of copper at
25.0°C. What would the final temperature of the copper be (in °C) if it absorbed
150.0 J of heat? a. | 19.7 | d. | 25.8 | b. | 5.3 | e. | -5.3 | c. | 30.3 | | | | |
|
|
|
42.
|
How
much energy (in kJ) is required to raise the temperature of 500.0 g of water from 20.00°C to
20.15°C? a. | 2.092 | d. | 0.3138 | b. | 331.8 | e. | 209.2 | c. | 75.00 | | | | |
|
|
|
43.
|
If
73.51 J of heat were added to 25.6 g of water at 25.3°C, what would be the final temperature of
the water? a. | 26.0°C | d. | 13.8°C | b. | 39.1°C | e. | -13.8°C | c. | 98.8°C | | | | |
|
|
|
44.
|
How
many grams of water can be heated from 20.0°C to 25.0°C by the addition of 324 J of
energy? a. | 15.5 | d. | 6.78 x
103 | b. | 20.9 | e. | 387 | c. | 1.36 x 103 | | | | |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match the
terms below with their correct definitions. a. | system | e. | kinetic energy | b. | calorimeter | f. | potential
energy | c. | thermochemistry | g. | surroundings | d. | universe | | | | |
|
|
|
45.
|
An insulated
device used to measure the amount of heat absorbed or released during a chemical or physical
process
|
|
|
46.
|
The study of
heat changes that accompany chemical reactions and phase changes
|
|
|
47.
|
The specific
part of the universe that contains the reaction or process you wish to study
|
|
|
48.
|
A system
plus its surroundings
|
|
|
49.
|
Everything
in the universe except the system being studied
|
|
|
50.
|
energy of motion
|