Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
A physical change occurs when a
A) | peach spoils. | C) | bracelet turns your wrist green. | B) | copper bowl
tarnishes. | D) | glue gun melts a
glue stick. |
|
|
|
2.
|
The base unit for mass is the
A) | gram. | C) | meter. | B) | cubic centimeter. | D) | kilogram. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which of the following is an extensive property of matter?
A) | melting point | C) | volume | B) | boiling point | D) | density |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which of the following is not a physical change?
A) | grinding | C) | boiling | B) | cutting | D) | burning |
|
|
|
5.
|
The symbols for units of length in order from largest to smallest are
A) | m, cm, mm, km. | C) | km, mm, cm, m. | B) | mm, m, cm, km. | D) | km, m, cm, mm. |
|
|
|
6.
|
What is the density of 37.72 g of material whose volume is 6.80
cm3?
A) | 0.180 g/cm3 | C) | 30.9 g/cm3 | B) | 5.55
g/cm3 | D) | 256.
g/cm3 |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of these measurements has been expressed to three significant
figures?
A) | 0.052 g | C) | 3.065 g | B) | 0.202 g | D) | 500 g |
|
|
|
8.
|
How is the measurement 0.000 065 cm written in scientific notation?
A) | 65 × 10–6 cm | C) | 6.5 × 10–6 cm | B) | 6.5 ×
10–5 cm | D) | 6.5 × 10–4
cm |
|
|
|
9.
|
When 1.92 × 10–6 kg is divided
by 6.8 × 102 mL, the quotient equals
A) | 2.8 × 10–4 kg/mL. | C) | 2.8 × 10–8 kg/mL. | B) | 2.8 × 10–5 kg/mL. | D) | 2.8 ×
10–9 kg/mL. |
|
|
|
10.
|
An aluminum isotope consists of 13 protons, 13 electrons, and 14 neutrons. Its
mass number is
|
|
|
11.
|
Neon-22 contains 12 neutrons. It also contains
A) | 12 protons. | C) | 22 electrons. | B) | 22 protons. | D) | 10 protons. |
|
|
|
12.
|
How many moles of atoms are in 50.15 g of mercury (atomic mass 200.59
amu)?
A) | 0.1001 mol | C) | 0.2500 mol | B) | 0.1504 mol | D) | 0.4000 mol |
|
|
|
13.
|
The speed of an electromagnetic wave is equal to the product of its wavelength
and its
A) | mass. | C) | velocity. | B) | color. | D) | frequency. |
|
|
|
14.
|
What values can the angular momentum quantum number have when n =
2?
A) | 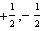 | C) | 0, 1, 2 | B) | 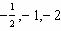 | D) | 0,
1 |
|
|
|
15.
|
The p orbitals are shaped like
A) | electrons. | C) | dumbbells. | B) | circles. | D) | spheres. |
|
|
|
16.
|
The statement that an electron occupies the lowest available energy orbital
is
A) | Hund's rule. | C) | Bohr's law. | B) | the Aufbau principle. | D) | the Pauli exclusion
principle. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Two electrons in the 1s orbital must have different spin quantum numbers
to satisfy
A) | quantum rule. | C) | the Pauli exclusion principle. | B) | the magnetic
rule. | D) | the Aufbau
principle. |
|
|
|
18.
|
The element with electron configuration 1s2
2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 is
A) | Mg (Z = 12). | C) | S (Z = 16). | B) | C (Z = 6). | D) | Si (Z =
14). |
|
|
|
19.
|
What is the electron configuration for nitrogen, atomic number 7?
A) | 1s2 2s2 2p3 | C) | 1s2 2s3 2p1 | B) | 1s2 2s3 2p2 | D) | 1s2 2s2
2p2 3s1 |
|
|
|
20.
|
The electron notation for aluminum (atomic number 13) is
A) | 1s2 2s2 2p3
3s2 3p3 3d1. | C) | 1s2
2s2 2p6 3s2
3p1. | B) | 1s2 2s2
2p6 3s2 2d1. | D) | 1s2 2s2
2p9. |
|
|
|
21.
|
The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is the atom's
A) | electron affinity. | C) | electronegativity. | B) | electron energy. | D) | ionization
energy. |
|
|
|
22.
|
The element that has the greatest electronegativity is
A) | oxygen. | C) | chlorine. | B) | sodium. | D) | fluorine. |
|
|
|
23.
|
In a row in the periodic table, as the atomic number increases, the atomic
radius generally
A) | decreases. | C) | increases. | B) | remains constant. | D) | becomes
immeasurable. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Within a group of elements, as the atomic number increases, the atomic
radius
A) | increases. | C) | decreases regularly. | B) | remains approximately
constant. | D) | varies
unpredictably. |
|
|
|
25.
|
To draw a Lewis structure, one must know the
A) | number of valence electrons in each atom. | C) | bond length of each
atom. | B) | atomic mass of each atom. | D) | ionization energy of each atom. |
|
|
|
26.
|
According to VSEPR theory, the shape of an AB3 molecule is
A) | trigonal-planar. | C) | linear. | B) | tetrahedral. | D) | bent. |
|
|
|
27.
|
According to VSEPR theory, the structure of the ammonia molecule,
NH3, is
A) | trigonal-planar. | C) | trigonal-pyramidal. | B) | bent. | D) | tetrahedral. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of the carbon tetraiodide molecule,
CI4.
A) | tetrahedral | C) | bent | B) | linear | D) | trigonal-planar |
|
|
|
29.
|
The hybridized orbitals responsible for the bent shape of the water molecule
are
A) | 1s2 2s2. | C) | sp3. | B) | ps1. | D) | 2s2
sp2. |
|
|
|
30.
|
What is the formula for zinc fluoride?
|
|
|
31.
|
Name the compound SO3.
A) | sulfur trioxide | C) | selenium trioxide | B) | silver trioxide | D) | sodium trioxide |
|
|
|
32.
|
What is the oxidation number of hydrogen in KH?
|
|
|
33.
|
What is the oxidation number of sulfur in H2SO4?
|
|
|
34.
|
What is the formula mass of (NH4)2SO4?
A) | 114.09 amu | C) | 128.06 amu | B) | 118.34 amu | D) | 132.16 amu |
|
|
|
35.
|
How many oxygen atoms are there in 0.500 mol of CO2?
A) | 6.02 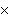 1023
1023 | C) | 15.9994 | B) | 3.01 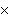 1023
1023 | D) | 11.0 |
|
|
|
36.
|
What is the percentage composition of CF4?
A) | 20% C, 80% F | C) | 16.8% C, 83.2% F | B) | 13.6% C, 86.4% F | D) | 81% C, 19% F |
|
|
|
37.
|
What is the empirical formula for a compound that is 31.9% potassium, 28.9%
chlorine, and 39.2% oxygen?
A) | KClO2 | C) | K2Cl2O3 | B) | KClO3 | D) | K2Cl2O5 |
|
|
|
38.
|
A compound's empirical formula is N2O5. If the
formula mass is 108 amu, what is the molecular formula?
|
|
|
39.
|
The complete balanced equation for the reaction between zinc hydroxide and
acetic acid is
A) | ZnOH + CH3COOH → ZnCH3COO +
H2O. | B) | Zn(OH)2 + CH3COOH → Zn +
2CO2 +3H2O. | C) | Zn(OH)2 + 2CH3COOH → Zn(CH3COO)2 + 2H2O. | D) | Zn(OH)2 +
2CH3COOH → Zn(CH3COO)2 +
H2 + O2. |
|
|
|
40.
|
The equation A + X → AX is the general equation
for a(n)
A) | combustion reaction. | C) | synthesis reaction. | B) | ionic reaction. | D) | double-displacement
reaction. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Oxides of active metals, such as CaO, react with water to produce
A) | metal carbonates. | C) | acids. | B) | metal hydrides. | D) | metal
hydroxides. |
|
|
|
42.
|
When a metal chlorate is heated, it decomposes to yield a metal chloride
and
A) | a metal oxide. | C) | hydrogen. | B) | a metal hydroxide. | D) | oxygen. |
|
|
|
43.
|
Predict the product of the reaction represented by the following equation:
MgO + CO2 →
A) | MgCO3 | C) | MgC + O3 | B) | Mg + CO3 | D) | MgCO2 +
O |
|
|
|
44.
|
What is the balanced equation when aluminum reacts with copper(II)
sulfate?
A) | Al + Cu2S → Al2S +
Cu | B) | 2Al + 3CuSO4 →
Al2(SO4)3 + 3Cu | C) | Al + CuSO4 → AlSO4 + Cu | D) | 2Al + Cu2SO4 → Al2SO4 + 2Cu |
|
|
|
45.
|
In the equation 2KClO3 → 2KCl +
3O2, how many moles of oxygen are produced when 3.0 mol of KClO3 decompose
completely?
A) | 1.0 mol | C) | 3.0 mol | B) | 2.5 mol | D) | 4.5 mol |
|
|
|
46.
|
For the reaction represented by the equation CH4 + 2O2
→ CO2 + 2H2O, how many moles of carbon dioxide
are produced from the combustion of 100. g of methane?
A) | 6.23 mol | C) | 12.5 mol | B) | 10.8 mol | D) | 25 mol |
|
|
|
47.
|
For the reaction represented by the equation SO3 + H2O
→ H2SO4, how many grams of sulfuric acid can
be produced from 200. g of sulfur trioxide and 100. g of water?
A) | 100. g | C) | 245 g | B) | 200. g | D) | 285 g |
|
|
|
48.
|
If the percentage yield is equal to 100%, then
A) | the actual yield is greater than the theoretical yield. | C) | the actual yield is
less than the theoretical yield. | B) | the actual yield is equal to the theoretical
yield. | D) | there was no
limiting reactant. |
|
|
|
49.
|
For the reaction represented by the equation SO3 + H2O
→ H2SO4, calculate the percentage yield if
500. g of sulfur trioxide react with excess water to produce 575 g of sulfuric acid.
A) | 82.7% | C) | 91.2% | B) | 88.3% | D) | 93.9% |
|
|
|
50.
|
The replacement of bromine by chlorine in a salt is an example of a
single-displacement reaction by
A) | halogens. | C) | water. | B) | sodium. | D) | electrolysis. |
|