Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
0.25 g is equivalent to
a. | 250 kg. | c. | 0.025 mg. | b. | 250 mg. | d. | 0.025 kg. |
|
|
|
2.
|
The number of significant figures in the measurement 0.000 305 kg is
|
|
|
3.
|
Which of these measurements has been expressed to three significant
figures?
a. | 0.052 g | c. | 3.065 g | b. | 0.202 g | d. | 500 g |
|
|
|
4.
|
When 64.4 is divided by 2.00, the correct number of significant figures in the
result is
|
|
|
5.
|
The dimensions of a rectangular solid are measured to be 1.27 cm, 1.3 cm, and
2.5 cm. The volume should be recorded as
a. | 4.128 cm3. | c. | 4.13 cm3. | b. | 4.12 cm3. | d. | 4.1
cm3. |
|
|
|
6.
|
A compound is
a. | a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, stable
substances. | b. | a substance, made of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded, that can be broken
down into simpler, stable substances. | c. | the smallest unit of matter that maintains its
chemical identity. | d. | any substance, whether it is chemically bonded
or not. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following is not a physical change?
a. | grinding | c. | boiling | b. | cutting | d. | burning |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following is not a chemical change?
a. | rusting | c. | melting | b. | igniting | d. | burning |
|
|
|
9.
|
A mixture is
a. | a combination of pure substances bonded chemically. | b. | any substance with a
uniform composition. | c. | a blend of any two or more kinds of matter, as
long as each maintains its own unique properties. | d. | any group of elements that are chemically
bonded to one another. |
|
|
|
10.
|
If a mixture is uniform in composition, it is said to be
a. | homogeneous. | c. | heterogeneous. | b. | chemically bonded. | d. | a compound. |
|
|
|
11.
|
An aluminum isotope consists of 13 protons, 13 electrons, and 14 neutrons. Its
mass number is
|
|
|
12.
|
Chlorine has atomic number 17 and mass number 35. It has
a. | 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 18 neutrons. | b. | 35 protons, 35
electrons, and 17 neutrons. | c. | 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 52
neutrons. | d. | 18 protons, 18 electrons, and 17 neutrons. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Phosphorus-33 (atomic number 15) contains
a. | 33 protons. | c. | 33 neutrons. | b. | 18 neutrons. | d. | 18 protons. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Neon-22 contains 12 neutrons. It also contains
a. | 12 protons. | c. | 22 electrons. | b. | 22 protons. | d. | 10 protons. |
|
|
|
15.
|
An element consists of two isotopes. The abundance of one isotope is 95.72% and
its atomic mass is 114.9041 u. The atomic mass of the second isotope is 112.9043 u. What is the
average atomic mass of the element?
a. | 113.9 u | b. | 113.0 u | c. | 113.9
u | d. | 114.8 u | e. | 115.1 u |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for the phosphate
ion? 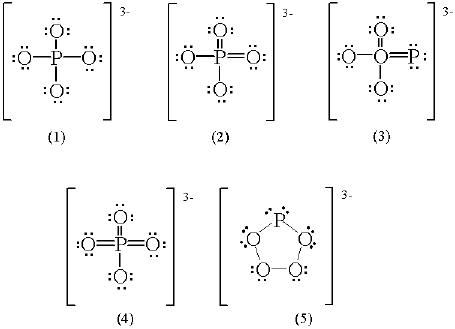
|
|
|
17.
|
The central atom in IF2- is surrounded by
a. | no single bonds, 2 double bonds, and no lone pairs of electrons. | b. | no single bonds, 2
double bonds, and 2 lone pairs of electrons. | c. | 1 single bond, 1 double bond, and 1 lone pair
of electrons. | d. | 2 single bonds, no double bonds, and 2 lone pairs of electrons. | e. | 2 single bonds, no
double bonds, and 3 lone pairs of electrons. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following species will have a Lewis structure most like that of
SF4?
a. | XeF4 | b. | SO42- | c. | ICl4+ | d. | PF4+ | e. | IO4- |
|
|
|
19.
|
Use VSEPR theory to predict the electron-pair geometry and the molecular
geometry of the nitrite ion, NO2-.
a. | The electron-pair geometry is linear, the molecular geometry is
linear. | b. | The electron-pair geometry is trigonal-planar, the molecular geometry is
bent. | c. | The electron-pair geometry is trigonal-planar, the molecular geometry is
linear. | d. | The electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral, the molecular geometry is
bent. | e. | The electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral, the molecular geometry is
linear. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Use VSEPR theory to predict the electron-pair geometry and the molecular
geometry of iodine trichloride, ICl3.
a. | The e--pair geometry is trigonal-planar, the molecular geometry is
trigonal-planar. | b. | The e--pair geometry is tetrahedral, the molecular geometry is
trigonal-pyramidal. | c. | The e--pair geometry is tetrahedral,
the molecular geometry is trigonal-planar. | d. | The e--pair geometry is
trigonal-bipyramidal, the molecular geometry is T-shaped. | e. | The
e--pair geometry is trigonal-bipyramidal, the molecular geometry is
trigonal-planar. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following formulas is not correct?
a. | Al2(SO4)3 | b. | NaClO3 | c. | Ba2O3 | d. | Mg(NO3)2 | e. | KH2PO4 |
|
|
|
22.
|
What is the correct formula for an ionic compound that contains aluminum ions
and carbonate ions?
a. | AlCO3 | b. | Al(CO3)2 | c. | Al(CO3)3 | d. | Al2(CO3)3 | e. | Al3(CO3)2 |
|
|
|
23.
|
What is the correct formula for sodium acetate?
a. | Na2CH3O | b. | NaCH3CO2 | c. | NaCH3O | d. | NaCH2O2 | e. | NaCHO |
|
|
|
24.
|
What is the correct formula for barium nitrate?
a. | Ba(NO3)2 | b. | BNO2 | c. | Ba(NO2)2 | d. | BaN | e. | BaNO3 |
|
|
|
25.
|
All of the following are named correctly EXCEPT
a. | LiClO4; lithium perchlorate. | b. | CaHPO4;
calcium hydrogen phosphide. | c. | NaCN; sodium cyanide. | d. | Mg(OH)2;
magnesium hydroxide. | e. | CaSO3; calcium
sulfite. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Ammonia is prepared by reacting nitrogen and hydrogen gases at high temperature
according to the unbalanced chemical equation below.
__ N2(g) + __ H2(g)
® __ NH3(g)
What are the respective coefficients
when the equation is balanced with the smallest whole numbers?
a. | 1, 1, 1 | b. | 1, 3, 1 | c. | 1, 3,
2 | d. | 2, 1, 2 | e. | 2, 3, 2 |
|
|
|
27.
|
If aqueous solutions of copper(II) nitrate and sodium carbonate are mixed, which
insoluble compound will form?
a. | CuCO3 | b. | Cu(NO3)2 | c. | NaNO3 | d. | Na2Cu | e. | Na2CO3 |
|
|
|
28.
|
What reaction occurs when aqueous solutions of sodium hydroxide and copper(II)
bromide are mixed?
a. | Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) +
2Br-(aq) ® NaCu(s) +
Br2OH(aq) | b. | Na+(aq) +
OH-(aq) + CuBr2(s) ®
NaBr2(aq) + CuOH(s) | c. | Na+(aq) +
Br-(aq) ® NaBr(s) | d. | 2Na+(aq) + Br2(aq) ® 2NaBr(s) | e. | 2OH-(aq) +
Cu2+(aq) ®
Cu(OH)2(s) |
|
|
|
29.
|
What net ionic reaction occurs when aqueous solutions of potassium carbonate and
iron(III) bromide are mixed?
a. | CO32-(aq) + 2Fe+(aq) ® Fe2(CO3)(s) | b. | 3CO32-(aq) + 2Fe3+(aq) ® Fe2(CO3)3(s) | c. | 3CO32-(aq) + 6Fe+(aq) ® 3Fe2CO3(s) | d. | 3K2CO3(aq) + 2Fe3+(aq) +
6Br-(aq) ®
Fe2(CO3)3(s) + 6KBr(s) | e. | no reaction
occurs |
|
|
|
30.
|
Write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction of aqueous solutions of
lead(II) nitrate and potassium chloride.
a. | Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KCl(aq) ® PbCl2(s) +
2KNO3(aq) | b. | Pb2+(aq) +
2K+(aq) ®
PbK2(s) | c. | Pb2+(aq) +
2Cl-(aq) ®
PbCl2(s) | d. | NO3-(aq) +
K+(aq) ®
KNO3(s) | e. | no precipitation
occurs. |
|
|
|
31.
|
What is the mass in grams of 0.338 mol of glucose
(C6H12O6)?
a. | 0.00188 g | b. | 0.0164 g | c. | 1.88
g | d. | 53.3 g | e. | 60.9 g |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which is a correct method for calculating the moles present in 132 grams of
calcium carbonate?
a. | 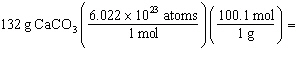 | b. | 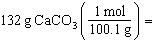 | c. | 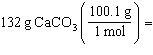 | d. | 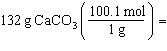 | e. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
33.
|
What is the percent composition of silicon nitride
(Si3N4)?
a. | 30.21% Si and 69.79% N | b. | 42.92% Si and 57.08% N | c. | 54.03% Si and 45.97%
N | d. | 60.06% Si and 39.94% N | e. | 69.40% Si and 30.60%
N |
|
|
|
34.
|
What is the percent composition of iron(II) sulfate hexahydrate?
a. | 4.2% Fe; 4.2% S; 41.6% O; 50.0% H | b. | 16.7% Fe; 16.7%S; 66.6% O | c. | 21.5% Fe; 12.3%S;
24.6% O; 41.6% H | d. | 21.5% Fe; 12.3%S; 61.5% O; 4.7% H | e. | 36.8% Fe; 21.1%S; 42.1%
O |
|
|
|
35.
|
Chalcopyrite is a mineral which contains 34.62% Cu, 30.43% Fe, and 34.95% S.
What is the chemical formula for chalcopyrite?
a. | CuFeS | b. | CuFeS2 | c. | CuFe2S | d. | Cu2FeS | e. | Cu2FeS2 |
|
|
|
36.
|
An oxide of nitrogen contains 63.1% oxygen and has a molar mass of 76.0 g/mol.
What is the molecular formula for this compound?
a. | N2O | b. | NO | c. | NO2 | d. | N2O3 | e. | N2O5 |
|
|
|
37.
|
If 16.4 g of oxygen gas react with excess hydrogen, what mass of water is
produced? 2H 2( g) + O 2( g) 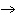
2H 2O( g) a. | 9.23 g | b. | 18.5 g | c. | 20.4
g | d. | 23.9 g | e. | 36.9 g |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which method is correct for determining the mass of carbon dioxide that can be
made by the combustion of 3.219 grams of ethanol with excess
oxygen?
C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) ® 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
|
|
|
39.
|
Sodium metal and water react to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. What
mass of Na will react with excess water to produce 15 g NaOH?
2Na(s) +
2H2O(l) ® H2(g) +
2NaOH(aq)
a. | 4.3 g | b. | 5.4 g | c. | 8.6
g | d. | 11 g | e. | 26 g |
|
|
|
40.
|
What is the empirical formula for a compound that is 31.9% potassium, 28.9%
chlorine, and 39.2% oxygen?
a. | KClO2 | c. | K2Cl2O3 | b. | KClO3 | d. | K2Cl2O5 |
|
|
|
41.
|
Which of the following does not increase the rate of dissolving a solid
in water?
a. | raising the temperature of the water | b. | stirring the solution | c. | using larger pieces
of solid | d. | crushing the solid |
|
|
|
42.
|
What is the molarity of a solution that contains 0.202 mol KCl in 7.98 L
solution?
a. | 0.0132 M | c. | 0.459 M | b. | 0.0253 M | d. | 1.363 M |
|
|
|
43.
|
What is the molarity of a solution that contains 125 g NaCl in 4.00 L solution?
(molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g/mol)
a. | 0.535 M | c. | 8.56 M | b. | 2.14 M | d. | 31.3 M |
|
|
|
44.
|
What is the mass of solute in 225 mL of 5.91 ´
10-2 M KIO3?
a. | 0.0133 g | b. | 0.0562 g | c. | 0.263
g | d. | 1.51 g | e. | 2.85 g |
|
|
|
45.
|
If 5.00 mL of 0.314 M KOH is diluted to exactly 125 mL with water, what is the
concentration of the resulting solution?
a. | 5.02 ´ 10-4 M | b. | 1.26 ´ 10-2 M | c. | 0.127 M | d. | 0.281
M | e. | 7.85 M |
|
|
|
46.
|
For a neutron (mass = 1.675 ´ 10-27
kg) moving with a velocity of 5.2 ´ 103 m/s, what is the
de Broglie wavelength?
a. | 7.6 ´ 10-11 m | b. | 4.5 ´ 10-9 m | c. | 2.1 ´
10-6 m | d. | 486 m | e. | 1.3 ´ 1010 m |
|
|
|
47.
|
What type of orbital is designated n = 4, l =
3, ml = -3?
|
|
|
48.
|
All of the following sets of quantum numbers are allowed EXCEPT
a. | n = 5, l = 3, ml = +2 | b. | n = 3, l = 2,
ml = -1 | c. | n = 3, l = 0,
ml = 0 | d. | n = 4, l = 4,
ml = -2 | e. | n = 5, l = 3,
ml = +3 |
|
|
|
49.
|
Which element has the following electron configuration? 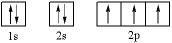
|
|
|
50.
|
Place the following atoms in order of increasing atomic radii: Ca, Mg, P, and
Cl.
a. | Cl < P < Mg < Ca | b. | Mg < P < Cl < Ca | c. | Ca < Mg < P
< Cl | d. | P < Cl < Mg < Ca | e. | Ca < Cl < P <
Mg |
|
|
|
51.
|
A balloon is filled with oxygen gas to a volume of 1.75 L at 36ºC. The
balloon is then heated to 72ºC. What is the volume of the heated balloon?
a. | 0.875 L | b. | 1.57 L | c. | 1.95
L | d. | 3.50 L | e. | 4.11 L |
|
|
|
52.
|
A 10.0 L flask contains 14.1 grams of an unknown gas. If the pressure in the
flask is 2.3 atm at 65ºC, which of the following is a possible identity of the gas?
|
|
|
53.
|
If 5.00 L of propane is burned in 21.0 L of oxygen, what volume of carbon
dioxide is produced? Assume that the temperature of the reactants and products is 25ºC and the
pressure of the system remains constant at 1.0 atm.
C3H8(g) +
5O2(g) ® 3CO2(g) +
4H2O(l)
a. | 12.6 L | b. | 15.0 L | c. | 21.0
L | d. | 25.6 L | e. | 26.0 L |
|
|
|
54.
|
Water can be decomposed by electrolysis to hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. What
mass of water must decompose to yield 24.0 L of oxygen gas at 1.00 atm and
25ºC?
2H2O(l) ®
2H2(g) + O2(g)
a. | 11.1 g | b. | 17.7 g | c. | 23.6
g | d. | 35.3 g | e. | 70.7 g |
|
|
|
55.
|
A 10.0 L flask is used to collect 0.500 moles of N2 and 0.180 moles
of O2 over water at 30ºC. What is the pressure in the flask? (vapor pressure
H2O(l) = 31.8 mm Hg)
a. | -30.1 atm | b. | 1.15 atm | c. | 1.48
atm | d. | 1.69 atm | e. | 1.73 atm |
|